Question 1:
Study the exhibit carefully. Both host stations are part of the same subnet but are in different VLANs. On the basis of the information presented in the exhibit, which statement is true about an attempt to ping from host to host?
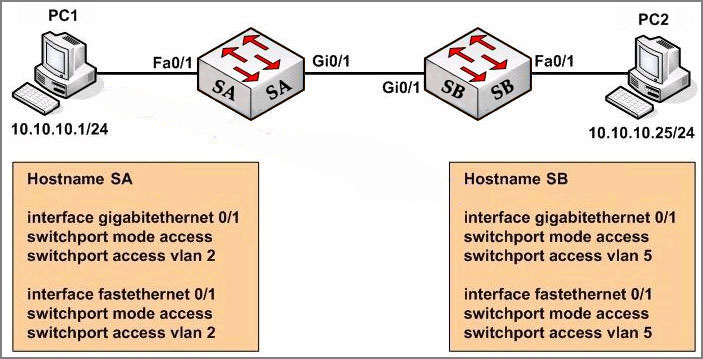 A – Layer 3 device is needed for the ping command to be successful.
A – Layer 3 device is needed for the ping command to be successful.
B – A trunk port will need to be configured on the link between SA and SB for the ping command to be successful.
C – The two different hosts will need to be in the same VLAN in order for the ping command to be successful.
D – The ping command will be successful without any further configuration changes.
Answer: D
Explanation:
For two hosts in different VLANs, we must use a layer 3 device to transport packages between them. However, in this case both switches are set in “access” mode therefore the VLAN information sent between them will be set as untagged. Moreover, they are in the same subnet so they can ping each other without a layer 3 device.
Question 2:
Based on the following exhibit, which problem is preventing users on VLAN 100 from pinging addresses on VLAN 200?
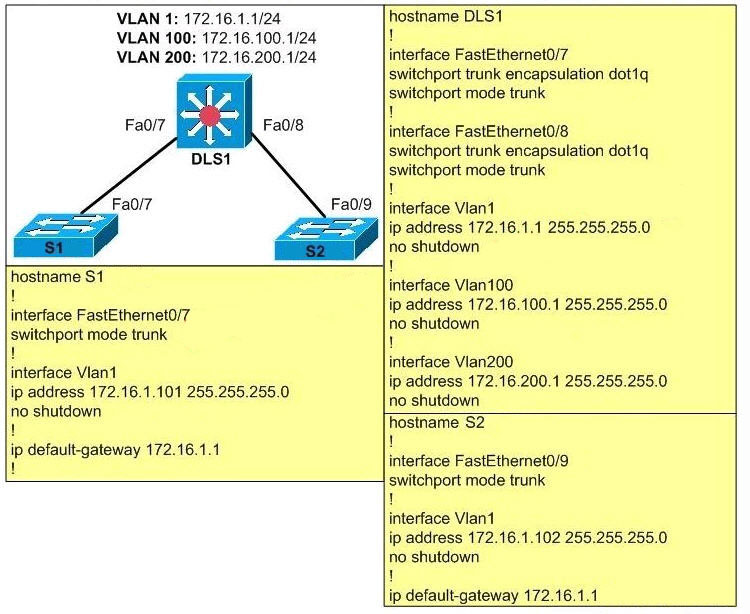 A – Native VLAN mismatch.
A – Native VLAN mismatch.
B – Subinterfaces should be created on Fa0/7 and Fa0/8 on DLS1.
C – Trunking needs to be enabled.
D – The ip routing command is missing on DLS1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
To allow communication between two VLANs, we need to enables Layer 3 routing on the switch with the “ip routing” command. Some flatforms are enabled by default but some are not.
Question 3:
Based on the network diagram and routing table output in the exhibit, which one of these statements is true?
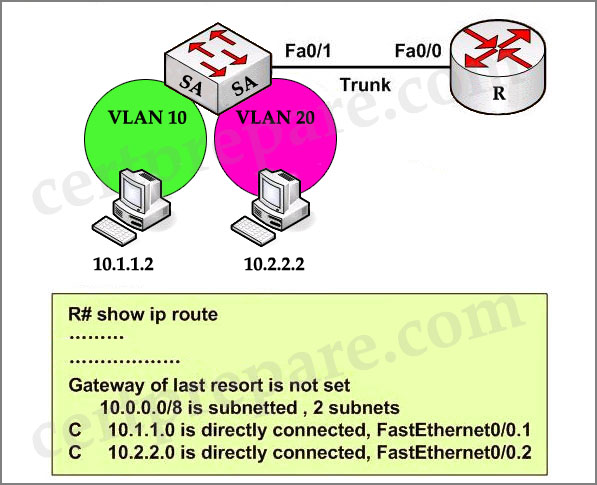 A – InterVLAN routing has been configured properly, and the workstations have connectivity to each other.
A – InterVLAN routing has been configured properly, and the workstations have connectivity to each other.
B – InterVLAN routing will not occur since no routing protocol has been configured.
C – Although interVLAN routing is not enabled, both workstations will have connectivity to each other.
D – Although interVLAN routing is enabled, the workstations will not have connectivity to each other.
E – None of the above.
Answer: A
Explanation:
In the output we can see both VLAN10 and VLAN20 are shown up (as networks 10.1.1.0 and 10.2.2.0) so the routing has been configured properly. Notice that the “C” letter indicates that these networks are directly connected with the router.
Question 4:
Study the following exhibit carefully, what is the reason that users from VLAN 100 can’t ping users on VLAN 200?
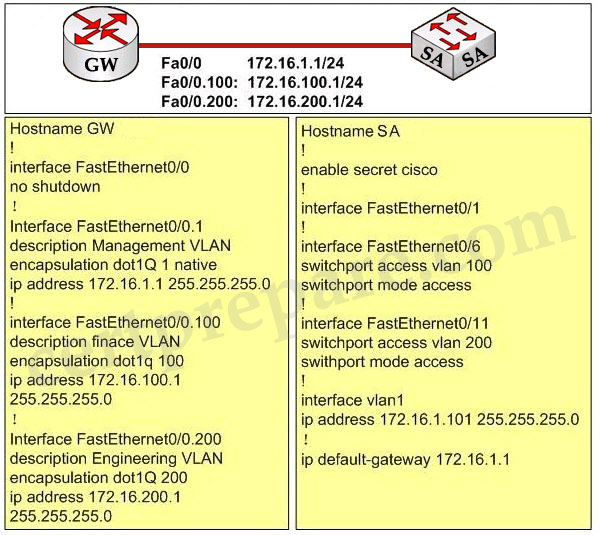 A – IP routing needs to be enabled on the switch
A – IP routing needs to be enabled on the switch
B – Trunking needs to be enabled on Fa0/1
C – VLAN 1 needs the no shutdown command
D – The native VLAN is wrong
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Fa0/1 interface on the switch is not configured with trunking mode. It needs to be configured as shown below:
SA(config)#interface Fa0/1
SA(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
SA(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Question 5:
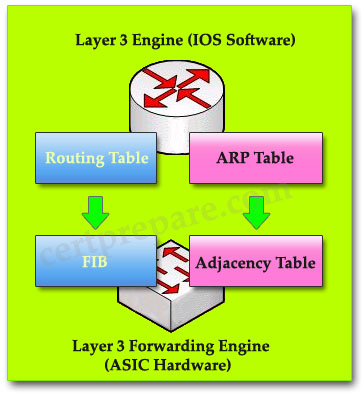
Assume that a host sends a packet to a destination IP address and that the CEF-based switch does not yet have a valid MAC address for the destination. How is the ARP entry (MAC address) of the next-hop destination in the FIB get?
A – The sending host must send an ARP request for it
B – All packets to the destination are dropped
C – The Layer 3 forwarding engine (CEF hardware) must send an ARP request for it
D – CEF must wait until the Layer 3 engine sends an ARP request for it
Answer: D
Explanation:
If a valid MAC address for the destination is not found, the Layer 3 forwarding engine can’t forward the packet in hardware due to the missing Layer 2 next-hop address. Therefore the packet is sent to the Layer 3 Engine so that it can generate an ARP request (this is called the “CEF glean” state)
Question 6:
Refer to the exhibit.
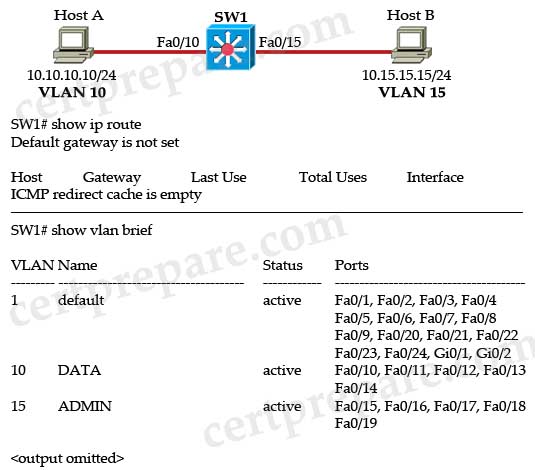 Host A and Host B are connected to the Cisco Catalyst 3550 switch and have been assigned to their respective VLANs. The rest of the 3550 configuration is the default configuration. Host A is able to ping its default gateway, 10.10.10.1, but is unable to ping Host B. Given the output in the exhibit, which statement is true?
Host A and Host B are connected to the Cisco Catalyst 3550 switch and have been assigned to their respective VLANs. The rest of the 3550 configuration is the default configuration. Host A is able to ping its default gateway, 10.10.10.1, but is unable to ping Host B. Given the output in the exhibit, which statement is true?
A. HSRP must be configured on SW1.
B. A separate router is needed to support inter-VLAN routing.
C. Interface VLAN 10 must be configured on the SW1 switch.
D. The global configuration command ip routing must be configured on the SW1 switch.
E. VLANs 10 and 15 must be created in the VLAN database mode.
F. VTP must be configured to support inter-VLAN routing.
Answer: D
Explanation
To enable routing on a Layer 3 switch first we have to use the ip routing command. From the output of “show vlan brief” command above, we learn that ports connected to hosts have been configured as access ports and assigned to VLAN 10 & 15. The missing thing here is only the “ip routing” command. Below lists the full configuration so that these two hosts can communicate.
Question 8
Which three statements about routed ports on a multilayer switch are true? (Choose three)
A. A routed port can support VLAN subinterfaces.
B. A routed port takes an IP address assignment.
C. A routed port can be configured with routing protocols.
D. A routed port is a virtual interface on the multilayer switch.
E. A routed port is associated only with one VLAN.
F. A routed port is a physical interface on the multilayer switch.
Answer: B C F
Explanation
A routed port on a multilayer switch has the same characteristic as a normal port on a router.
Question 9
Which two statements describe a routed switch port on a multilayer switch? (Choose two)
A. Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 routing are mutually supported.
B. The port is not associated with any VLAN.
C. The routed switch port supports VLAN subinterfaces.
D. The routed switch port is used when a switch has only one port per VLAN or subnet.
E. The routed switch port ensures that STP remains in the forwarding state.
Answer: B D
Explanation
A routed switch port on a Layer 3 switch is same as a port on a router. By default, ports on a multilayer switch will all be running in Layer 2 mode. To configure a port as a routed port, use the “no switchport” command. From now, the port is not associated with any VLAN -> B is correct.
Also like ports in a router, each port can only belongs to one VLAN or subnet -> D is correct.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
Which statement is true?
A. Cisco Express Forwarding load balancing has been disabled.
B. SVI VLAN 30 connects directly to the 10.1.30.0/24 network due to a valid glean adjacency.
C. VLAN 30 is not operational because no packet or byte counts are indicated.
D. The IP Cisco Express Forwarding configuration is capable of supporting IPv6.
Answer: B
Explanation
When a router is connected directly to several hosts, the FIB table on the router maintains a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefixes. The subnet prefix points to a glean adjacency. When packets need to be forwarded to a specific host, the adjacency database is gleaned for the specific prefix.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.
You have configured an interface to be an SVI for Layer 3 routing capabilities. Assuming that all VLANs have been correctly configured, what can be determined?
A. Interface gigabitethemet0/2 will be excluded from Layer 2 switching and enabled for Layer 3 routing.
B. The command switchport autostate exclude should be entered in global configuration mode, not subinterface mode, to enable a Layer 2 port to be configured for Layer 3 routing.
C. The configured port is excluded in the calculation of the status of the SVI.
D. The interface is missing IP configuration parameters; therefore, it will only function at Layer 2.
Answer: C
Explanation
An SVI is considered “up” as long as at least one port in its associated VLAN is active and forwarding. If all ports in the VLAN are down, the interface goes down to avoid creating a routing black hole. You might not want the status of a particular port (one not connected to a host) to affect the SVI’s status. The switchport autostate exclude command enables you to exclude the access ports/trunks in defining the status of the SVI (up or down) even if it belongs to the same VLAN.
Question 12
Which two steps are necessary to configure inter-VLAN routing between multilayer switches? (Choose two)
A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol.
B. Configure SVI interfaces with IP addresses and subnet masks.
C. Configure access ports with network addresses.
D Configure switch ports with the autostate exclude command.
E. Document the MAC addresses of the switch ports.
Answer: A B
Explanation
A multilayer switch can use a switched virtual interface (SVI) to provide inter-VLAN routing rather than use an external router. Below is a simple example of using SVIs to configure inter-VLAN routing on a Layer 3 switch.
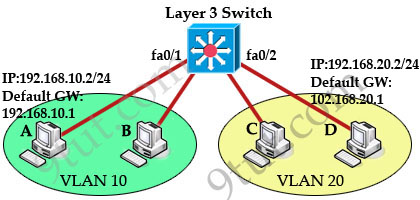
(In fact we need to configure two more interfaces so that all hosts can communicate)
Also, the above configuration is only for a single multilayer switch. If we enable interVLAN-routing between two multilayer switches, a routing protocol needs to be used.
Question 13
When configuring a routed port on a Cisco multilayer switch, which configuration task is needed to enable that port to function as a routed port?
A. Enable the switch to participate in routing updates from external devices with the router command in global configuration mode.
B. Enter the no switchport command to disable Layer 2 functionality at the interface level.
C. Each port participating in routing of Layer 3 packets must have an IP routing protocol assigned on a per-interface level.
D. Routing is enabled by default on a multilayer switch, so the port can become a Layer 3 routing interface by assigning the appropriate IP address and subnet information.
Answer: B
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit, which is from a Cisco Catalyst 3560 Series Switch.
Switch#configure terminal
Switch(config)#interface gigabitethernet0/2
Switch(config-if)#no switchport
Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.20.135.21 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
Which statement about the Layer 3 routing functionality of the interface is true?
A. The interface is configured correctly for Layer 3 routing capabilities.
B. The interface needs an additional configuration entry to enable IP routing protocols.
C. Since the interface is connected to a host device, the spanning-tree portfast command must be added to the interface.
D. An SVI interface is needed to enable IP routing for network 192.20.135.0.
Answer: A
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit
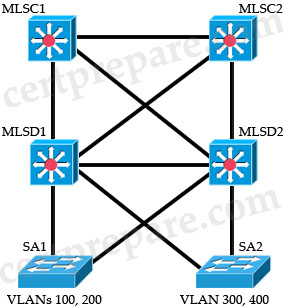
For the configuration shown, which is the recommended method of providing inter VLAN routing?
A. Determine which switch is the root bridge then connect a router on a stick to it
B. Configure SVIs on the core switches
C. Configure SVIs on the distribution switches
D. Configure SVIs on the access layer switches
Answer: C
Explanation
We can configure SVIs on Multilayer switches to use as the default gateways or Layer 3 routing for the devices connected to SA1 & SA2.
Study the exhibit carefully. Both host stations are part of the same subnet but are in different VLANs. On the basis of the information presented in the exhibit, which statement is true about an attempt to ping from host to host?

B – A trunk port will need to be configured on the link between SA and SB for the ping command to be successful.
C – The two different hosts will need to be in the same VLAN in order for the ping command to be successful.
D – The ping command will be successful without any further configuration changes.
Answer: D
Explanation:
For two hosts in different VLANs, we must use a layer 3 device to transport packages between them. However, in this case both switches are set in “access” mode therefore the VLAN information sent between them will be set as untagged. Moreover, they are in the same subnet so they can ping each other without a layer 3 device.
Question 2:
Based on the following exhibit, which problem is preventing users on VLAN 100 from pinging addresses on VLAN 200?

B – Subinterfaces should be created on Fa0/7 and Fa0/8 on DLS1.
C – Trunking needs to be enabled.
D – The ip routing command is missing on DLS1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
To allow communication between two VLANs, we need to enables Layer 3 routing on the switch with the “ip routing” command. Some flatforms are enabled by default but some are not.
Question 3:
Based on the network diagram and routing table output in the exhibit, which one of these statements is true?

B – InterVLAN routing will not occur since no routing protocol has been configured.
C – Although interVLAN routing is not enabled, both workstations will have connectivity to each other.
D – Although interVLAN routing is enabled, the workstations will not have connectivity to each other.
E – None of the above.
Answer: A
Explanation:
In the output we can see both VLAN10 and VLAN20 are shown up (as networks 10.1.1.0 and 10.2.2.0) so the routing has been configured properly. Notice that the “C” letter indicates that these networks are directly connected with the router.
Question 4:
Study the following exhibit carefully, what is the reason that users from VLAN 100 can’t ping users on VLAN 200?

B – Trunking needs to be enabled on Fa0/1
C – VLAN 1 needs the no shutdown command
D – The native VLAN is wrong
Answer: B
Explanation:
The Fa0/1 interface on the switch is not configured with trunking mode. It needs to be configured as shown below:
SA(config)#interface Fa0/1
SA(config-if)#switchport mode trunk
SA(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
Question 5:
Assume that a host sends a packet to a destination IP address and that the CEF-based switch does not yet have a valid MAC address for the destination. How is the ARP entry (MAC address) of the next-hop destination in the FIB get?
A – The sending host must send an ARP request for it
B – All packets to the destination are dropped
C – The Layer 3 forwarding engine (CEF hardware) must send an ARP request for it
D – CEF must wait until the Layer 3 engine sends an ARP request for it
Answer: D
Explanation:
If a valid MAC address for the destination is not found, the Layer 3 forwarding engine can’t forward the packet in hardware due to the missing Layer 2 next-hop address. Therefore the packet is sent to the Layer 3 Engine so that it can generate an ARP request (this is called the “CEF glean” state)

Question 6:
CEF is a complete new routing switch technology . Which two table types are CEF components?(Choose two)
A – adjacency tables
B – caching tables
C – neighbor tables
D – forwarding information base
B – caching tables
C – neighbor tables
D – forwarding information base
Answer: A D
Question 7Refer to the exhibit.

A. HSRP must be configured on SW1.
B. A separate router is needed to support inter-VLAN routing.
C. Interface VLAN 10 must be configured on the SW1 switch.
D. The global configuration command ip routing must be configured on the SW1 switch.
E. VLANs 10 and 15 must be created in the VLAN database mode.
F. VTP must be configured to support inter-VLAN routing.
Answer: D
Explanation
To enable routing on a Layer 3 switch first we have to use the ip routing command. From the output of “show vlan brief” command above, we learn that ports connected to hosts have been configured as access ports and assigned to VLAN 10 & 15. The missing thing here is only the “ip routing” command. Below lists the full configuration so that these two hosts can communicate.
| ip routing ! interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/15 switchport access vlan 15 switchport mode access ! interface Vlan10 ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan15 ip address 10.15.15.1 255.255.255.0 |
Which three statements about routed ports on a multilayer switch are true? (Choose three)
A. A routed port can support VLAN subinterfaces.
B. A routed port takes an IP address assignment.
C. A routed port can be configured with routing protocols.
D. A routed port is a virtual interface on the multilayer switch.
E. A routed port is associated only with one VLAN.
F. A routed port is a physical interface on the multilayer switch.
Answer: B C F
Explanation
A routed port on a multilayer switch has the same characteristic as a normal port on a router.
Question 9
Which two statements describe a routed switch port on a multilayer switch? (Choose two)
A. Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 routing are mutually supported.
B. The port is not associated with any VLAN.
C. The routed switch port supports VLAN subinterfaces.
D. The routed switch port is used when a switch has only one port per VLAN or subnet.
E. The routed switch port ensures that STP remains in the forwarding state.
Answer: B D
Explanation
A routed switch port on a Layer 3 switch is same as a port on a router. By default, ports on a multilayer switch will all be running in Layer 2 mode. To configure a port as a routed port, use the “no switchport” command. From now, the port is not associated with any VLAN -> B is correct.
Also like ports in a router, each port can only belongs to one VLAN or subnet -> D is correct.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit.
| Switch# show ip cef vlan 30 detail IP CEF with switching (Table Version 11), flags=0×0 10 routes, 0 reresolve, 0 unresolved (0 old, 0 new), peak 0 13 leaves, 12 nodes, 14248 bytes, 14 inserts, 1 invalidations 0 load sharing elements, 0 bytes, 0 references universal per-destination load sharing algorithm, id 4B936A24 2(0) CEF resets, 0 revisions of existing leaves Resolution Timer: Exponential (currently 1s, peak 1s) 0 in-place/0 aborted modifications refcounts: 1061 leaf, 1052 node Table epoch: 0 (13 entries at this epoch) 10.1.30.0/24, version 6, epoch 0, attached, connected 0 packets, 0 bytes via Vlan30,0 dependencies valid glean adjacency |
A. Cisco Express Forwarding load balancing has been disabled.
B. SVI VLAN 30 connects directly to the 10.1.30.0/24 network due to a valid glean adjacency.
C. VLAN 30 is not operational because no packet or byte counts are indicated.
D. The IP Cisco Express Forwarding configuration is capable of supporting IPv6.
Answer: B
Explanation
When a router is connected directly to several hosts, the FIB table on the router maintains a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefixes. The subnet prefix points to a glean adjacency. When packets need to be forwarded to a specific host, the adjacency database is gleaned for the specific prefix.
Question 11
Refer to the exhibit.
| Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# interface gigabitethernet0/2 Switch(config-if)# switchport autostate exclude Switch(config-if)# exit |
A. Interface gigabitethemet0/2 will be excluded from Layer 2 switching and enabled for Layer 3 routing.
B. The command switchport autostate exclude should be entered in global configuration mode, not subinterface mode, to enable a Layer 2 port to be configured for Layer 3 routing.
C. The configured port is excluded in the calculation of the status of the SVI.
D. The interface is missing IP configuration parameters; therefore, it will only function at Layer 2.
Answer: C
Explanation
An SVI is considered “up” as long as at least one port in its associated VLAN is active and forwarding. If all ports in the VLAN are down, the interface goes down to avoid creating a routing black hole. You might not want the status of a particular port (one not connected to a host) to affect the SVI’s status. The switchport autostate exclude command enables you to exclude the access ports/trunks in defining the status of the SVI (up or down) even if it belongs to the same VLAN.
Question 12
Which two steps are necessary to configure inter-VLAN routing between multilayer switches? (Choose two)
A. Configure a dynamic routing protocol.
B. Configure SVI interfaces with IP addresses and subnet masks.
C. Configure access ports with network addresses.
D Configure switch ports with the autostate exclude command.
E. Document the MAC addresses of the switch ports.
Answer: A B
Explanation
A multilayer switch can use a switched virtual interface (SVI) to provide inter-VLAN routing rather than use an external router. Below is a simple example of using SVIs to configure inter-VLAN routing on a Layer 3 switch.

| ip routing ! interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport access vlan 10 switchport mode access ! interface FastEthernet0/2 switchport access vlan 20 switchport mode access interface Vlan10 ip address 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 ! interface Vlan20 ip address 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 |
Also, the above configuration is only for a single multilayer switch. If we enable interVLAN-routing between two multilayer switches, a routing protocol needs to be used.
Question 13
When configuring a routed port on a Cisco multilayer switch, which configuration task is needed to enable that port to function as a routed port?
A. Enable the switch to participate in routing updates from external devices with the router command in global configuration mode.
B. Enter the no switchport command to disable Layer 2 functionality at the interface level.
C. Each port participating in routing of Layer 3 packets must have an IP routing protocol assigned on a per-interface level.
D. Routing is enabled by default on a multilayer switch, so the port can become a Layer 3 routing interface by assigning the appropriate IP address and subnet information.
Answer: B
Question 14
Refer to the exhibit, which is from a Cisco Catalyst 3560 Series Switch.
Switch#configure terminal
Switch(config)#interface gigabitethernet0/2
Switch(config-if)#no switchport
Switch(config-if)#ip address 192.20.135.21 255.255.255.0
Switch(config-if)#no shutdown
Which statement about the Layer 3 routing functionality of the interface is true?
A. The interface is configured correctly for Layer 3 routing capabilities.
B. The interface needs an additional configuration entry to enable IP routing protocols.
C. Since the interface is connected to a host device, the spanning-tree portfast command must be added to the interface.
D. An SVI interface is needed to enable IP routing for network 192.20.135.0.
Answer: A
Question 15
Refer to the exhibit

For the configuration shown, which is the recommended method of providing inter VLAN routing?
A. Determine which switch is the root bridge then connect a router on a stick to it
B. Configure SVIs on the core switches
C. Configure SVIs on the distribution switches
D. Configure SVIs on the access layer switches
Answer: C
Explanation
We can configure SVIs on Multilayer switches to use as the default gateways or Layer 3 routing for the devices connected to SA1 & SA2.
