Question 1
Switch R1 and R2 both belong to the Company VTP domain. What’s true about the switch operation in VTP domains? (Choose two)
A. A switch can only reside in one management domain
B. A switch is listening to VTP advertisements from their own domain only
C. A switch is listening to VTP advertisements from multi domains
D. A switch can reside in one or more domains
E. VTP is no longer supported on Catalyst switches
Answer: A B
Explanation
A VTP domain (also called a VLAN management domain) is made up of one or more network devices that share the same VTP domain name and that are interconnected with trunks. A network device can be configured to be in one and only one VTP domain -> A is correct.
If the switch receives a VTP advertisement over a trunk link, it inherits the management domain name and the VTP configuration revision number. The switch ignores advertisements with a different management domain name or an earlier configuration revision number -> B is correct.
Note: Just for your information, if a switch has not belonged to any VTP domain yet and it receives a VTP advertisement with a VTP domain (whose password is not set), it will join that domain automatically.
Question 2
How does VTP pruning enhance network bandwidth?
A. by restricting unicast traffic to across VTP domains
B. by reducing unnecessary flooding of traffic to inactive VLANs
C. by limiting the spreading of VLAN information
D. by disabling periodic VTP updates
Answer: B
Explanation
VTP Pruning makes more efficient use of trunk bandwidth by forwarding broadcast and unknown unicast frames on a VLAN only if the switch on the receiving end of the trunk has ports in that VLAN.
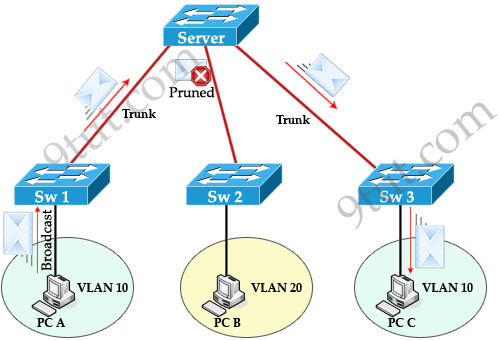
The following example shows the operation of a VTP domain without and with VTP Pruning.
Without VTP Pruning:

Question 3
VTP devices in a network track the VTP revision number. What is a VTP configuration revision number?
A. A number for identifying changes to the network switch.
B. A number for identifying changes to the network router.
C. A number for identifying changes to the network topology.
Answer: C
Question 4
VTP switches use advertisements to exchange information with each other. Which of the following advertisement types are associated with VTP? (Choose three)
A. Domain advertisements
B. Advertisement requests from clients
C. Subset advertisements
D. Summary advertisements
Answer: B C D
Explanation
All VTP packets contain these fields in the header:
* VTP protocol version: 1, 2, or 3
* VTP message types:
1) Summary advertisements (inform adjacent Catalysts of the current VTP domain name and the configuration revision number)
2) Subset advertisement (is sent following the summary advertisement and contains a list of VLAN information)
3) Advertisement requests (is needed in the case it is reset, the VTP domain name has been changed or it has received a VTP summary advertisement with a higher configuration revision than it own).
4) VTP join messages (similar to the Advertisement request messages but with a different Message Type field value and a few more parameters, including VTP domain name, and a VLAN bit string. If the bit is set, flooded traffic for that VLAN should be received on that trunk. Each trunk port maintains a state variable per VLAN – Joined/Pruned. If the state is Joined, the trunk port is allowed to send broadcast and flooded unicast traffic on this VLAN. If the state is Pruned, the trunk port will not send the broadcast or flooded unicast traffic on this VLAN. VTP join messages are sent when the VTP Client first joins a VTP domain to inform the VTP Servers about its existence in that VTP domain).
* Management domain length
* Management domain name
Question 5
The lack of which two prevents VTP information from propagating between switches? (Choose two)
A. A root VTP server
B. A trunk port
C. VTP priority
D. VLAN 1
Answer: B D
Explanation
VTP advertisements only travel through trunk ports -> B is correct.
VLAN 1 is a special VLAN selected by design to carry specific information such as CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol), VTP, PAgP and DTP. This is always the case and cannot be changed. Cisco recommends not to use VLAN 1 as a standard VLAN to carry network data -> D is correct.
Question 6
Which two DTP modes will permit trunking between directly connected switches? (Choose two)
A. dynamic desirable (VTP domain A) to dynamic desirable (VTP domain A)
B. dynamic desirable (VTP domain A) to dynamic desirable (VTP domain B)
C. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to dynamic auto (VTP domain A)
D. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to dynamic auto (VTP domain B)
E. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to nonegotiate (VTP domain A)
F. nonegotiate (VTP domain A) to nonegotiate (VTP domain B)
Answer: A F
Explanation
Below is the switchport modes for easy reference:
Note: If an interface is set to switchport mode dynamic desirable, it will actively attempt to convert the link into trunking mode. If the peer port is configured as switchport mode trunk, dynamic desirable, or dynamic auto mode, trunking is negotiated successfully -> A is correct.
B is not correct because 2 dynamic desirable mode in 2 different VTP domains cannot create a trunk link.
Dynamic auto waits to receive DTP from the neighbor so if 2 interfaces are set to this mode, none of them will receive DTP frames -> C and D are not correct.
A port in Nonegotiate mode can be set to access or trunk port mode but it will not send DTP. Dynamic auto also does not send DTP -> a trunk link cannot be created -> E is not correct.
Also, when setting ports to nonegotiate, that port will not send DTP. We can set both interfaces to trunk link -> a trunk link can be created between two different VTP domains -> F is correct.
Question 7
The Company switches are configured to use VTP. What’s true about the VLAN trunking protocol (VTP)? (Choose two)
A. VTP messages will not be forwarded over nontrunk links.
B. VTP domain names need to be identical. However, case doesn’t matter.
C. A VTP enabled device which receives multiple advertisements will ignore advertisements with higher configuration revision numbers.
D. A device in “transparent” VTP v.1 mode will not forward VTP messages.
E. VTP pruning allows switches to prune VLANs that do not have any active ports associated with them.
Answer: A D
Explanation
Answer A is obviously correct as VTP advertisements only travel through trunk ports.
VTP domain names are case-sensitive. That means the domain “certprepare” is different from “Certprepare”. There is no exception -> B is not correct.
A VTP enabled device which receives multiple advertisements will update (not ignore) advertisements with higher configuration revision numbers, provided that it has the same VTP domain name and password -> C is not correct.
Answer D is not clear. In VTP Version 1, a VTP transparent switch inspects VTP messages for the domain name and version and forwards a message only if the version and domain name match. Because VTP Version 2 supports only one domain, it forwards VTP messages in transparent mode without inspecting the version and domain name. So in this case we don’t have enough information to conclude about answer D.
Answer E is not clear too. VTP will prune VLANs on trunks connected to switches that do not have ports associated with the VLANs. I am not sure what Cisco wants to say in answer E.
But if we consider answer E to be incorrect then the best answers should be A and D.

Question 8
The Company switches have all been upgraded to use VTP version 2. What are two benefits provided in VTP Version 2 that are not available in VTP Version 1? (Choose two)
A. VTP version 2 supports Token Ring VLANs.
B. VTP version 2 allows VLAN consistency checks.
C. VTP version 2 saves VLAN configuration memory.
D. VTP version 2 reduces the amount of configuration necessary.
E. The VTP version 2 allows active redundant links when used with spanning tree.
Answer: A B
Explanation
The major difference is that VTP V2 introduces support for Token Ring VLANs. If you use Token Ring VLANs, you must enable VTP V2 -> A is correct.
In VTP version 2, VLAN consistency checks (such as VLAN names and values) are performed only when you enter new information through the command-line interface (CLI) or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Consistency checks are not performed when new information is obtained from a VTP message or when information is read from NVRAM. If the digest on a received VTP message is correct, its information is accepted without consistency checks -> B is correct.
Question 9
Switch R1 is configured to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP). What does R1 advertise in its VTP domain?
A. The VLAN ID of all known VLANs, the management domain name, and the total number of trunk links on the switch.
B. The VLAN ID of all known VLANs, a 1-bit canonical format (CF1 Indicator), and the switch configuration revision number.
C. The management domain name, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters.
D. A 2-byte TPID with a fixed value of 0×8100 for the management domain number, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters.
Answer: C
Explanation
VTP advertises its management domain name, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters -> C is correct.
Note: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (not VTP) tag uses the tag protocol identifier (TPID) field to identify the protocol type. The Default TPID value in IEEE 802.1Q, is 0×8100 -> D is not correct.
Question 10
Which two statements correctly describe VTP? (Choose two.)
A. Transparent mode always has a configuration revision number of 0.
B. Transparent mode cannot modify a VLAN database.
C. Client mode cannot forward received VTP advertisements.
D. Client mode synchronizes its VLAN database from VTP advertisements.
E. Server mode can synchronize across VTP domains.
Answer: A D
Question 11
What action should a network administrator take to enable VTP pruning on an entire management domain?
A. Enable VTP pruning on any switch in the management domain.
B. Enable VTP pruning on any client switch in the management domain.
C. Enable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain.
D. Enable VTP pruning on every switch in the management domain.
E. Disable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain.
Answer: C
Explanation
VTP pruning should only be enabled on VTP servers, all the clients in the VTP domain will automatically enable VTP pruning -> C is correct.
Question 12
What must be configured on a Cisco switch in order to advertise VLAN information?
A. VTP mode
B. VTP password
C. VTP revision number
D. VTP pruning
E. VTP domain name
Answer: E
Explanation
A Cisco switch needs a VTP domain name to advertise VLAN information to other switches and it must be configured on a Cisco switch.
Note: If a switch is configured as a VTP server without a VTP domain name, you cannot configure a VLAN on the switch
Question 13
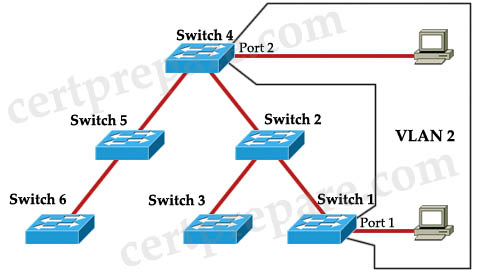
Refer to the exhibit. VTP has been enabled on the trunk links between all switches within the Certprepare domain. An administrator has recently enabled VTP pruning. Port 1 on Switch 1 and port 2 on Switch 4 are assigned to VLAN 2. A broadcast is sent from the host connected to Switch 1. Where will the broadcast propagate?
 A. Every switch in the network receives the broadcast and will forward it out all ports.
A. Every switch in the network receives the broadcast and will forward it out all ports.
B. Every switch in the network receives the broadcast, but only Switch 4 will forward it out port 2.
C. Switches 1, 2, and 4 will receive the broadcast, but only Switch 4 will forward it out port 2.
D. Only Switch 4 will receive the broadcast and will forward it out port 2.
Answer: C
Explanation
With VTP pruning enabled network-wide, switch 2 and switch 4 automatically use VTP to learn that none of the switches in the lower-left part of the figure have any ports assigned to VLAN 10. As a result, switch 2 and switch 4 prune VLAN 2 from the trunks connected to these switches. The pruning causes switch 2 and switch 4 to not send frames in VLAN 2 out these trunks -> Switches 3, 5 and 6 will not receive the broadcast while Switch 4 will receive it and forward out to port 2 -> C is correct.
Question 14
Switch R1 is part of the Company VTP domain. What’s true of VTP Pruning within this domain?
A. It does not prune traffic from VLANs that are pruning-ineligible
B. VLAN 1 is always pruning-eligible
C. It will prune traffic from VLANs that are pruning-ineligible
D. VLAN 2 is always pruning-ineligible
Answer: A
Explanation
VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002 to 1005 are always pruning-ineligible; traffic from these VLANs cannot be pruned. Extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs greater than 1005) are also pruning-ineligible -> A is correct.
Question 15
Switch R1 has been configured with DTP using the desirable option. Which statement describes Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) desirable mode?
A. The interface actively attempts to convert the link to a trunk link.
B. The interface is put into permanent trunking mode but prevented from generating DTP frames.
C. The interface is put into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link.
D. The interface is put into a passive mode, waiting to convert the link to a trunk link.
Answer: A
Explanation
Note: If an interface is set to switchport mode dynamic desirable, it will actively attempt to convert the link into trunking mode. If the peer port is configured as switchport mode trunk, dynamic desirable, or dynamic auto mode, trunking is negotiated successfully.
Question 16
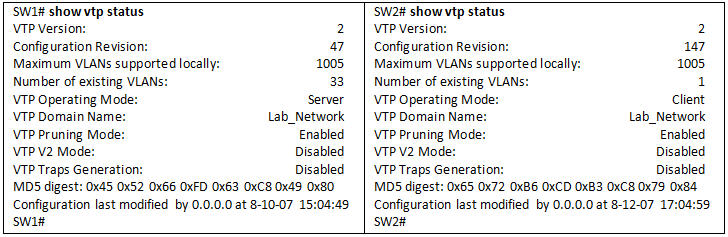
Refer to the exhibit. What happens when the switch SW2 is connected to the rest of the network in the VTP domain Lab_Network?
A. The recently introduced switch SW2 adds one more VLAN to the VLAN database in the VTP domain.
B. The recently introduced switch SW2 creates a STP loop in the VTP domain.
C. The recently introduced switch SW2 removes all configured VLANs throughout the VTP domain.
D. The recently introduced switch SW2 switches over to VTP transparent mode in order to be included into the VTP domain.
E. A trunk should be configured between the two switches in order to integrate SW2 into the VTP domain.
Answer: C
Explanation
The Configuration Revision number of SW2 is higher than that of SW1 (147 > 47) and SW2 is operating in Client mode so it can send update to other switches. The result is SW1 and other switches in that VTP domain will remove their current VLAN information and copy VLAN information from SW2.
Question 17
What is the default VTP advertisement for subset advertisements in Catalyst switches that are in server or client mode?
A. 30 seconds
B. 5 minutes
C. 1 minute
D. 10 seconds
E. 5 seconds
Answer: B
Explanation
Subset advertisements list the specific changes that have been performed, such as creating or deleting a VLAN, suspending or activating a VLAN, changing the name of a VLAN, and changing a VLAN’s maximum transmission unit (MTU), status of the VLAN, VLAN type (such as Ethernet or Token Ring), length of the VLAN name, VLAN number, security association identifier (SAID) value. Summary advertisements are sent out every 300 seconds (5 minutes) by default.
Question 18
Two Company switches are connected via a trunk using VTP. Which VTP information does a Catalyst switch advertise on its trunk ports when using VTP? (Choose two)
A. STP root status
B. VTP mode
C. Negotiation status
D. Management domain
E. Configuration revision number
Answer: D E
Question 19
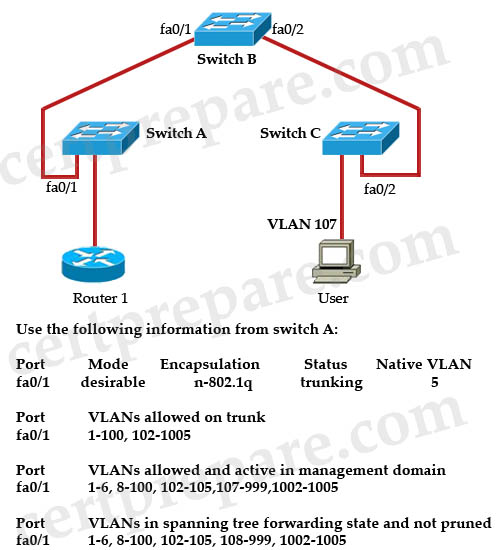
The network operations center has received a call stating that users in VLAN 107 are unable to access resources through Router 1. From the information contained in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?
 A. VLAN 107 does not exist on switch A.
A. VLAN 107 does not exist on switch A.
B. VTP is pruning VLAN 107.
C. VLAN 107 is not configured on the trunk.
D. Spanning tree is not enabled on VLAN 107.
Answer: B
Explanation
From the “VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned” we can deduce that VLAN 107 is currently pruned on switch A.
Question 20
A switch that is to be added to the production network has been preconfigured (trunks, VLANs, VTP, and STP) and was tested in your lab. After installing the switch into the network, the entire network went down. What might explain what happened?
A. The new switch happened to be running Cisco Catalyst operating system, while the other network switches were running Cisco IOS Software.
B. The configuration revision of the new switch was higher than the configuration revision of the production VTP domain.
C. The link costs on the new switch are set to a high value, causing all ports on the new switch to go into a forwarding mode and none into blocking mode, thereby causing a spanning-tree loop.
D. The ports connecting to the two switches have been configured incorrectly. One side has the command switchport mode access and the other switchport mode trunk.
Answer: B
Explanation
If the configuration revision number of the new switch is higher than that of the rest of Cisco switches and it is in Client or Server mode with the same VTP domain then it can wipe out other switches’ VLAN information. This is a nightmare if you are working for a large company and it can make you to lose your job so please remember this: always set your newly added Cisco switch to VTP Transparent mode before plugging into your working network. This step also resets the Configuration Revision Number of that switch back to 0, which is safe to plug into your network.
Question 21
Which two statements correctly describe VTP? (Choose two)
A. Transparent mode always has a configuration revision number of 0.
B. Transparent mode cannot modify a VLAN database.
C. Client mode cannot forward received VTP advertisements.
D. Client mode synchronizes its VLAN database from VTP advertisements.
E. Server mode can synchronize across VTP domains.
Answer: A D
Explanation
When setting a switch to Transparent mode, the switch’s configuration revision number is automatically reset to 0 -> A is correct.
Not only client mode but server mode synchronize its VLAN database from VTP advertisements -> D is correct.
Question 22
The network administrator needs to enable VTP pruning within the network. What action should a network administrator take to enable VTP pruning on an entire management domain?
A – enable VTP pruning on every switch in the domain
B – enable VTP pruning on any client switch in the domain
C – enable VTP pruning on any switch in the management domain
D – enable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain
Answer: D
Question 23
The network operations center has received a call stating that Users in VLAN 107 are unable to access resources through R1. From the information contained in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?
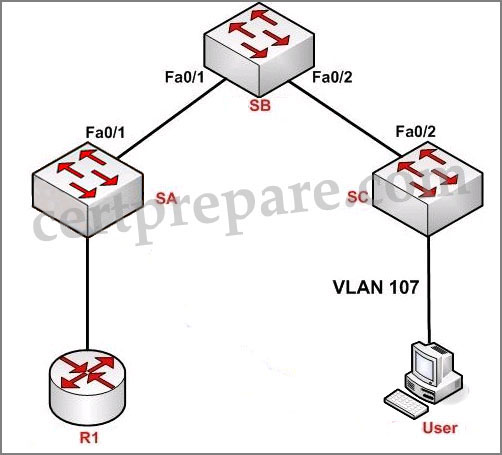
 A – spanning tree is not enabled on VLAN 107
A – spanning tree is not enabled on VLAN 107
B – VTP is pruning VLAN 107
C – VLAN 107 does not exist on switch SA
D – VLAN 107 is not configured on the trunk
Answer: B
Explanation:
“VLAN allowed on trunk” – Each trunk allows all VLANs by default. However, administrator can remove or add to the list by using the “switchport trunk allowed” command.
“VLANs allowed and active in management” – To be active, a VLAN must be in this list.
“VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned” – This list is a subset of the “allowed and active” list but with any VTP-pruned VLANs removed.
All VLANs were configured except VLAN 101 so D is not correct. VLAN 107 exists in the “allowed and active” section so A and C are not correct, too. In the “forwarding state and not pruned” we don’t see VLAN 107 so the administrator had wrongly configured this VLAN as pruned.
Switch R1 and R2 both belong to the Company VTP domain. What’s true about the switch operation in VTP domains? (Choose two)
A. A switch can only reside in one management domain
B. A switch is listening to VTP advertisements from their own domain only
C. A switch is listening to VTP advertisements from multi domains
D. A switch can reside in one or more domains
E. VTP is no longer supported on Catalyst switches
Answer: A B
Explanation
A VTP domain (also called a VLAN management domain) is made up of one or more network devices that share the same VTP domain name and that are interconnected with trunks. A network device can be configured to be in one and only one VTP domain -> A is correct.
If the switch receives a VTP advertisement over a trunk link, it inherits the management domain name and the VTP configuration revision number. The switch ignores advertisements with a different management domain name or an earlier configuration revision number -> B is correct.
Note: Just for your information, if a switch has not belonged to any VTP domain yet and it receives a VTP advertisement with a VTP domain (whose password is not set), it will join that domain automatically.
Question 2
How does VTP pruning enhance network bandwidth?
A. by restricting unicast traffic to across VTP domains
B. by reducing unnecessary flooding of traffic to inactive VLANs
C. by limiting the spreading of VLAN information
D. by disabling periodic VTP updates
Answer: B
Explanation
VTP Pruning makes more efficient use of trunk bandwidth by forwarding broadcast and unknown unicast frames on a VLAN only if the switch on the receiving end of the trunk has ports in that VLAN.
The following example shows the operation of a VTP domain without and with VTP Pruning.
Without VTP Pruning:

VTP domain without VTP Pruning
When PC A sends a broadcast frame on VLAN 10, it travels across all trunk links in the VTP domain. Switches Server, Sw2, and Sw3 all receive broadcast frames from PC A. But only Sw3 has user on VLAN 10 and it is a waste of bandwidth on Sw2. Moreover, that broadcast traffic also consumes processor time on Sw2. The link between switches Server and Sw2 does not carry any VLAN 10 traffic so it can be “pruned”.
VTP domain with VTP Pruning
-> B is correct.Question 3
VTP devices in a network track the VTP revision number. What is a VTP configuration revision number?
A. A number for identifying changes to the network switch.
B. A number for identifying changes to the network router.
C. A number for identifying changes to the network topology.
Answer: C
Question 4
VTP switches use advertisements to exchange information with each other. Which of the following advertisement types are associated with VTP? (Choose three)
A. Domain advertisements
B. Advertisement requests from clients
C. Subset advertisements
D. Summary advertisements
Answer: B C D
Explanation
All VTP packets contain these fields in the header:
* VTP protocol version: 1, 2, or 3
* VTP message types:
1) Summary advertisements (inform adjacent Catalysts of the current VTP domain name and the configuration revision number)
2) Subset advertisement (is sent following the summary advertisement and contains a list of VLAN information)
3) Advertisement requests (is needed in the case it is reset, the VTP domain name has been changed or it has received a VTP summary advertisement with a higher configuration revision than it own).
4) VTP join messages (similar to the Advertisement request messages but with a different Message Type field value and a few more parameters, including VTP domain name, and a VLAN bit string. If the bit is set, flooded traffic for that VLAN should be received on that trunk. Each trunk port maintains a state variable per VLAN – Joined/Pruned. If the state is Joined, the trunk port is allowed to send broadcast and flooded unicast traffic on this VLAN. If the state is Pruned, the trunk port will not send the broadcast or flooded unicast traffic on this VLAN. VTP join messages are sent when the VTP Client first joins a VTP domain to inform the VTP Servers about its existence in that VTP domain).
* Management domain length
* Management domain name
Question 5
The lack of which two prevents VTP information from propagating between switches? (Choose two)
A. A root VTP server
B. A trunk port
C. VTP priority
D. VLAN 1
Answer: B D
Explanation
VTP advertisements only travel through trunk ports -> B is correct.
VLAN 1 is a special VLAN selected by design to carry specific information such as CDP (Cisco Discovery Protocol), VTP, PAgP and DTP. This is always the case and cannot be changed. Cisco recommends not to use VLAN 1 as a standard VLAN to carry network data -> D is correct.
Question 6
Which two DTP modes will permit trunking between directly connected switches? (Choose two)
A. dynamic desirable (VTP domain A) to dynamic desirable (VTP domain A)
B. dynamic desirable (VTP domain A) to dynamic desirable (VTP domain B)
C. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to dynamic auto (VTP domain A)
D. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to dynamic auto (VTP domain B)
E. dynamic auto (VTP domain A) to nonegotiate (VTP domain A)
F. nonegotiate (VTP domain A) to nonegotiate (VTP domain B)
Answer: A F
Explanation
Below is the switchport modes for easy reference:
| Mode | Function |
| Dynamic Auto | Creates the trunk based on the DTP request from the neighboring switch. |
| Dynamic Desirable | Communicates to the neighboring switch via DTP that the interface would like to become a trunk if the neighboring switch interface is able to become a trunk. |
| Trunk | Automatically enables trunking regardless of the state of the neighboring switch and regardless of any DTP requests sent from the neighboring switch. |
| Access | Trunking is not allowed on this port regardless of the state of the neighboring switch interface and regardless of any DTP requests sent from the neighboring switch. |
| Nonegotiate | Forces the port to permanently trunk but prevents the interface from generating DTP frames. This command can be used only when the interface switchport mode is access or trunk. You must manually configure the neighboring interface as a trunk interface to establish a trunk link. |
B is not correct because 2 dynamic desirable mode in 2 different VTP domains cannot create a trunk link.
Dynamic auto waits to receive DTP from the neighbor so if 2 interfaces are set to this mode, none of them will receive DTP frames -> C and D are not correct.
A port in Nonegotiate mode can be set to access or trunk port mode but it will not send DTP. Dynamic auto also does not send DTP -> a trunk link cannot be created -> E is not correct.
Also, when setting ports to nonegotiate, that port will not send DTP. We can set both interfaces to trunk link -> a trunk link can be created between two different VTP domains -> F is correct.
Question 7
The Company switches are configured to use VTP. What’s true about the VLAN trunking protocol (VTP)? (Choose two)
A. VTP messages will not be forwarded over nontrunk links.
B. VTP domain names need to be identical. However, case doesn’t matter.
C. A VTP enabled device which receives multiple advertisements will ignore advertisements with higher configuration revision numbers.
D. A device in “transparent” VTP v.1 mode will not forward VTP messages.
E. VTP pruning allows switches to prune VLANs that do not have any active ports associated with them.
Answer: A D
Explanation
Answer A is obviously correct as VTP advertisements only travel through trunk ports.
VTP domain names are case-sensitive. That means the domain “certprepare” is different from “Certprepare”. There is no exception -> B is not correct.
A VTP enabled device which receives multiple advertisements will update (not ignore) advertisements with higher configuration revision numbers, provided that it has the same VTP domain name and password -> C is not correct.
Answer D is not clear. In VTP Version 1, a VTP transparent switch inspects VTP messages for the domain name and version and forwards a message only if the version and domain name match. Because VTP Version 2 supports only one domain, it forwards VTP messages in transparent mode without inspecting the version and domain name. So in this case we don’t have enough information to conclude about answer D.
Answer E is not clear too. VTP will prune VLANs on trunks connected to switches that do not have ports associated with the VLANs. I am not sure what Cisco wants to say in answer E.
But if we consider answer E to be incorrect then the best answers should be A and D.

Question 8
The Company switches have all been upgraded to use VTP version 2. What are two benefits provided in VTP Version 2 that are not available in VTP Version 1? (Choose two)
A. VTP version 2 supports Token Ring VLANs.
B. VTP version 2 allows VLAN consistency checks.
C. VTP version 2 saves VLAN configuration memory.
D. VTP version 2 reduces the amount of configuration necessary.
E. The VTP version 2 allows active redundant links when used with spanning tree.
Answer: A B
Explanation
The major difference is that VTP V2 introduces support for Token Ring VLANs. If you use Token Ring VLANs, you must enable VTP V2 -> A is correct.
In VTP version 2, VLAN consistency checks (such as VLAN names and values) are performed only when you enter new information through the command-line interface (CLI) or Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Consistency checks are not performed when new information is obtained from a VTP message or when information is read from NVRAM. If the digest on a received VTP message is correct, its information is accepted without consistency checks -> B is correct.
Question 9
Switch R1 is configured to use the VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP). What does R1 advertise in its VTP domain?
A. The VLAN ID of all known VLANs, the management domain name, and the total number of trunk links on the switch.
B. The VLAN ID of all known VLANs, a 1-bit canonical format (CF1 Indicator), and the switch configuration revision number.
C. The management domain name, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters.
D. A 2-byte TPID with a fixed value of 0×8100 for the management domain number, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters.
Answer: C
Explanation
VTP advertises its management domain name, the switch configuration revision number, the known VLANs, and their specific parameters -> C is correct.
Note: IEEE 802.1Q VLAN (not VTP) tag uses the tag protocol identifier (TPID) field to identify the protocol type. The Default TPID value in IEEE 802.1Q, is 0×8100 -> D is not correct.
Question 10
Which two statements correctly describe VTP? (Choose two.)
A. Transparent mode always has a configuration revision number of 0.
B. Transparent mode cannot modify a VLAN database.
C. Client mode cannot forward received VTP advertisements.
D. Client mode synchronizes its VLAN database from VTP advertisements.
E. Server mode can synchronize across VTP domains.
Answer: A D
Question 11
What action should a network administrator take to enable VTP pruning on an entire management domain?
A. Enable VTP pruning on any switch in the management domain.
B. Enable VTP pruning on any client switch in the management domain.
C. Enable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain.
D. Enable VTP pruning on every switch in the management domain.
E. Disable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain.
Answer: C
Explanation
VTP pruning should only be enabled on VTP servers, all the clients in the VTP domain will automatically enable VTP pruning -> C is correct.
Question 12
What must be configured on a Cisco switch in order to advertise VLAN information?
A. VTP mode
B. VTP password
C. VTP revision number
D. VTP pruning
E. VTP domain name
Answer: E
Explanation
A Cisco switch needs a VTP domain name to advertise VLAN information to other switches and it must be configured on a Cisco switch.
Note: If a switch is configured as a VTP server without a VTP domain name, you cannot configure a VLAN on the switch
Question 13
Refer to the exhibit. VTP has been enabled on the trunk links between all switches within the Certprepare domain. An administrator has recently enabled VTP pruning. Port 1 on Switch 1 and port 2 on Switch 4 are assigned to VLAN 2. A broadcast is sent from the host connected to Switch 1. Where will the broadcast propagate?

B. Every switch in the network receives the broadcast, but only Switch 4 will forward it out port 2.
C. Switches 1, 2, and 4 will receive the broadcast, but only Switch 4 will forward it out port 2.
D. Only Switch 4 will receive the broadcast and will forward it out port 2.
Answer: C
Explanation
With VTP pruning enabled network-wide, switch 2 and switch 4 automatically use VTP to learn that none of the switches in the lower-left part of the figure have any ports assigned to VLAN 10. As a result, switch 2 and switch 4 prune VLAN 2 from the trunks connected to these switches. The pruning causes switch 2 and switch 4 to not send frames in VLAN 2 out these trunks -> Switches 3, 5 and 6 will not receive the broadcast while Switch 4 will receive it and forward out to port 2 -> C is correct.
Question 14
Switch R1 is part of the Company VTP domain. What’s true of VTP Pruning within this domain?
A. It does not prune traffic from VLANs that are pruning-ineligible
B. VLAN 1 is always pruning-eligible
C. It will prune traffic from VLANs that are pruning-ineligible
D. VLAN 2 is always pruning-ineligible
Answer: A
Explanation
VLAN 1 and VLANs 1002 to 1005 are always pruning-ineligible; traffic from these VLANs cannot be pruned. Extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs greater than 1005) are also pruning-ineligible -> A is correct.
Question 15
Switch R1 has been configured with DTP using the desirable option. Which statement describes Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP) desirable mode?
A. The interface actively attempts to convert the link to a trunk link.
B. The interface is put into permanent trunking mode but prevented from generating DTP frames.
C. The interface is put into permanent trunking mode and negotiates to convert the link into a trunk link.
D. The interface is put into a passive mode, waiting to convert the link to a trunk link.
Answer: A
Explanation
Note: If an interface is set to switchport mode dynamic desirable, it will actively attempt to convert the link into trunking mode. If the peer port is configured as switchport mode trunk, dynamic desirable, or dynamic auto mode, trunking is negotiated successfully.
Question 16
Refer to the exhibit. What happens when the switch SW2 is connected to the rest of the network in the VTP domain Lab_Network?

A. The recently introduced switch SW2 adds one more VLAN to the VLAN database in the VTP domain.
B. The recently introduced switch SW2 creates a STP loop in the VTP domain.
C. The recently introduced switch SW2 removes all configured VLANs throughout the VTP domain.
D. The recently introduced switch SW2 switches over to VTP transparent mode in order to be included into the VTP domain.
E. A trunk should be configured between the two switches in order to integrate SW2 into the VTP domain.
Answer: C
Explanation
The Configuration Revision number of SW2 is higher than that of SW1 (147 > 47) and SW2 is operating in Client mode so it can send update to other switches. The result is SW1 and other switches in that VTP domain will remove their current VLAN information and copy VLAN information from SW2.
Question 17
What is the default VTP advertisement for subset advertisements in Catalyst switches that are in server or client mode?
A. 30 seconds
B. 5 minutes
C. 1 minute
D. 10 seconds
E. 5 seconds
Answer: B
Explanation
Subset advertisements list the specific changes that have been performed, such as creating or deleting a VLAN, suspending or activating a VLAN, changing the name of a VLAN, and changing a VLAN’s maximum transmission unit (MTU), status of the VLAN, VLAN type (such as Ethernet or Token Ring), length of the VLAN name, VLAN number, security association identifier (SAID) value. Summary advertisements are sent out every 300 seconds (5 minutes) by default.
Question 18
Two Company switches are connected via a trunk using VTP. Which VTP information does a Catalyst switch advertise on its trunk ports when using VTP? (Choose two)
A. STP root status
B. VTP mode
C. Negotiation status
D. Management domain
E. Configuration revision number
Answer: D E
Question 19
The network operations center has received a call stating that users in VLAN 107 are unable to access resources through Router 1. From the information contained in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?

B. VTP is pruning VLAN 107.
C. VLAN 107 is not configured on the trunk.
D. Spanning tree is not enabled on VLAN 107.
Answer: B
Explanation
From the “VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned” we can deduce that VLAN 107 is currently pruned on switch A.
Question 20
A switch that is to be added to the production network has been preconfigured (trunks, VLANs, VTP, and STP) and was tested in your lab. After installing the switch into the network, the entire network went down. What might explain what happened?
A. The new switch happened to be running Cisco Catalyst operating system, while the other network switches were running Cisco IOS Software.
B. The configuration revision of the new switch was higher than the configuration revision of the production VTP domain.
C. The link costs on the new switch are set to a high value, causing all ports on the new switch to go into a forwarding mode and none into blocking mode, thereby causing a spanning-tree loop.
D. The ports connecting to the two switches have been configured incorrectly. One side has the command switchport mode access and the other switchport mode trunk.
Answer: B
Explanation
If the configuration revision number of the new switch is higher than that of the rest of Cisco switches and it is in Client or Server mode with the same VTP domain then it can wipe out other switches’ VLAN information. This is a nightmare if you are working for a large company and it can make you to lose your job so please remember this: always set your newly added Cisco switch to VTP Transparent mode before plugging into your working network. This step also resets the Configuration Revision Number of that switch back to 0, which is safe to plug into your network.
Question 21
Which two statements correctly describe VTP? (Choose two)
A. Transparent mode always has a configuration revision number of 0.
B. Transparent mode cannot modify a VLAN database.
C. Client mode cannot forward received VTP advertisements.
D. Client mode synchronizes its VLAN database from VTP advertisements.
E. Server mode can synchronize across VTP domains.
Answer: A D
Explanation
When setting a switch to Transparent mode, the switch’s configuration revision number is automatically reset to 0 -> A is correct.
Not only client mode but server mode synchronize its VLAN database from VTP advertisements -> D is correct.
Question 22
The network administrator needs to enable VTP pruning within the network. What action should a network administrator take to enable VTP pruning on an entire management domain?
A – enable VTP pruning on every switch in the domain
B – enable VTP pruning on any client switch in the domain
C – enable VTP pruning on any switch in the management domain
D – enable VTP pruning on a VTP server in the management domain
Answer: D
Question 23
The network operations center has received a call stating that Users in VLAN 107 are unable to access resources through R1. From the information contained in the graphic, what is the cause of this problem?


B – VTP is pruning VLAN 107
C – VLAN 107 does not exist on switch SA
D – VLAN 107 is not configured on the trunk
Answer: B
Explanation:
“VLAN allowed on trunk” – Each trunk allows all VLANs by default. However, administrator can remove or add to the list by using the “switchport trunk allowed” command.
“VLANs allowed and active in management” – To be active, a VLAN must be in this list.
“VLANs in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned” – This list is a subset of the “allowed and active” list but with any VTP-pruned VLANs removed.
All VLANs were configured except VLAN 101 so D is not correct. VLAN 107 exists in the “allowed and active” section so A and C are not correct, too. In the “forwarding state and not pruned” we don’t see VLAN 107 so the administrator had wrongly configured this VLAN as pruned.
